Examples package¶
Examples index
Submodules¶
Examples.Example48 module¶
Examples.Example49 module¶
Examples.Example50 module¶
Examples.Example50-2 module¶
Examples.Example59 module¶
Examples.Example60 module¶
Examples.Example60 h module¶
Examples.Example61 module¶
Examples.Example62 module¶
Examples.Example63 module¶
Examples.Example64 module¶
Examples.Example65 module¶
Examples.Example66 module¶
Examples.MITC6 module¶
- Examples.MITC6.assemble_B_bending(dNdxy)¶
- Examples.MITC6.assemble_B_membrane(dNdxy)¶
- Examples.MITC6.assemble_B_shear(dNdxy, N)¶
- Examples.MITC6.assemble_Ktangent_Fint(x_current, u_disp, D_membrane, D_bending, D_shear)¶
Assembles the tangent stiffness matrix and internal force vector for MITC6 5-DOF shell element (large displacement, updated geometry).
Inputs: - x_current: (6x3) array of current nodal coordinates (deformed shape) - u_disp: (30,) displacement vector - D_membrane: (3x3) material matrix (membrane) - D_bending: (3x3) material matrix (bending) - D_shear: (2x2) material matrix (shear)
Outputs: - K_tangent: (30x30) tangent stiffness matrix - F_int: (30,) internal force vector
- Examples.MITC6.build_global_transformation(basis)¶
Builds the 30x30 rotation matrix T for 5-DOF shell element: - Translations (u,v,w) rotated with basis, - Rotations (theta_x, theta_y) remain local.
Inputs: - basis: (3x3) matrix with e1, e2, e3 as columns.
Output: - T: (30x30) global transformation matrix
- Examples.MITC6.compute_local_coordinates(X)¶
- Examples.MITC6.generate_flat_panel()¶
Generate a simple flat triangular panel (ground plane) with 6-node MITC6 layout.
- Examples.MITC6.get_D_matrices(E=210000000000.0, nu=0.3, t=0.01, kappa=0.8333333333333334)¶
- Examples.MITC6.shape_functions_MITC6(r, s)¶
Examples.Punto3 module¶
Examples.Punto6 module¶
Examples.ShellAndHinge module¶
Examples.ShellAndHinge2 module¶
Examples.ShellAndHinge2 copy module¶
Examples.ShellAndHinge3 module¶
Examples.example1 module¶
Creation of 2D elements¶
Coords and gdls (degrees of freedom) are given by a Numpy ndarray matrix.
In the coordinate matrix, each row represents a node of the element and each column a dimension. For example, a 2D triangular element of 3 nodes must have a 3x2 matrix.
In the gdls matrix, each row represents a variable of the node and each column a node. For example, a 2D triangular element of 3 nodes and 2 variables per node (plane stress) must have a 2x3 gdls matrix.
In this example several characteristics are tested:
The element creation and transformations are tested over 2 triangular (2D), 2 quadrilateral (2D) and 2 lineal (1D) elements.
The isBetwwen methods gives the oportunity to check if a given set of points is are inside a element.
The inverseMapping method allows to give a set of global coordinates and convert them to natural coordinates.
The jacobian graph allows to verigfy the numerical estability of the element
Coordinate trasformation and shape functions¶
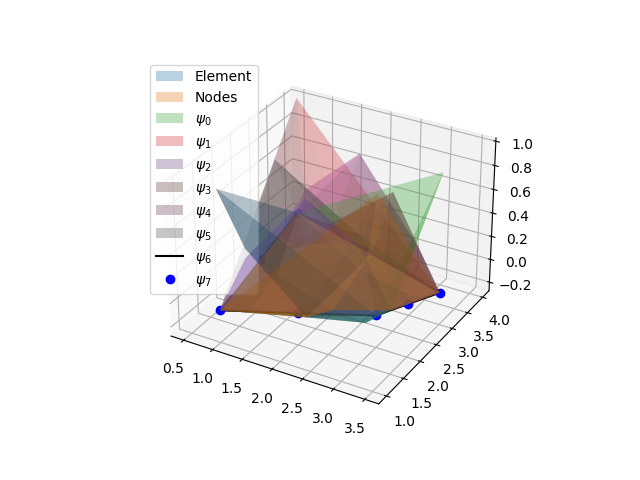
Serendipity (8 nodes 2D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
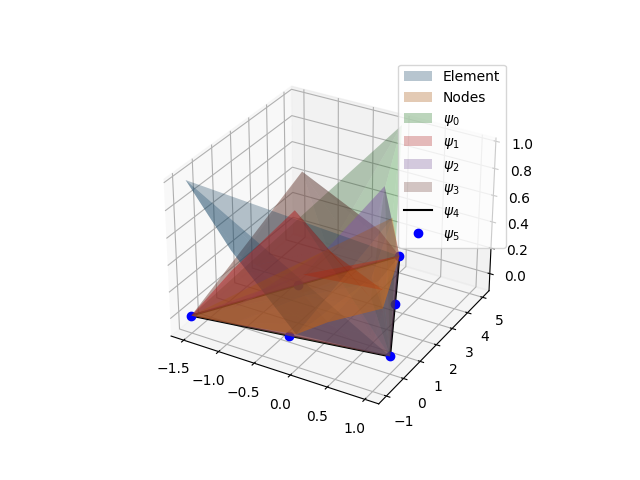
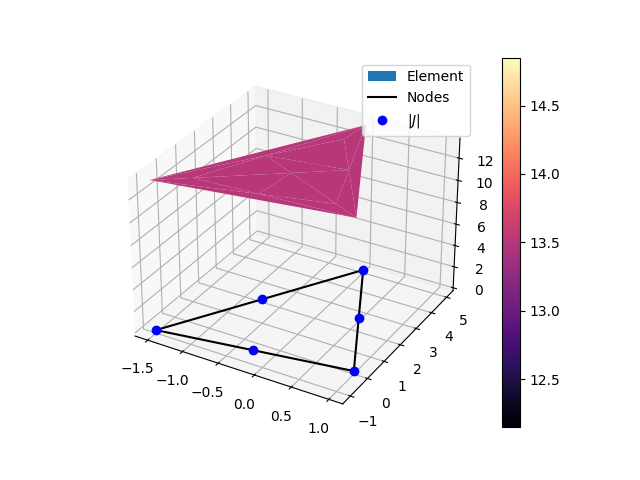
Quadrilateral (4 nodes 2D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
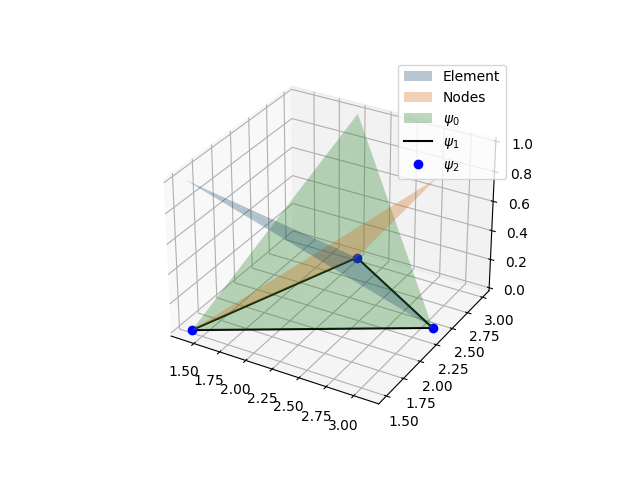
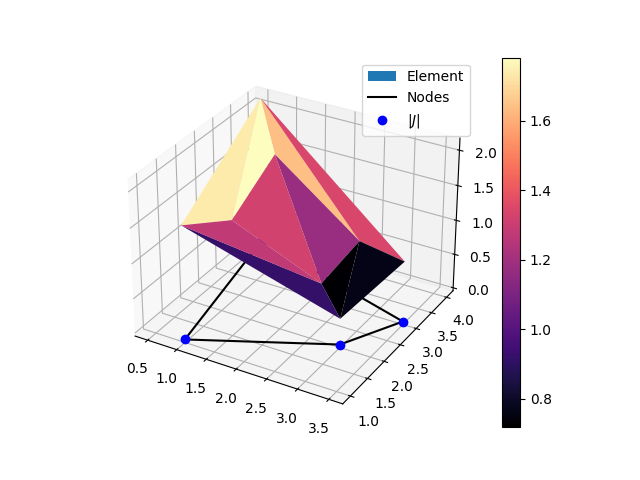
Triangular (6 nodes 2D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
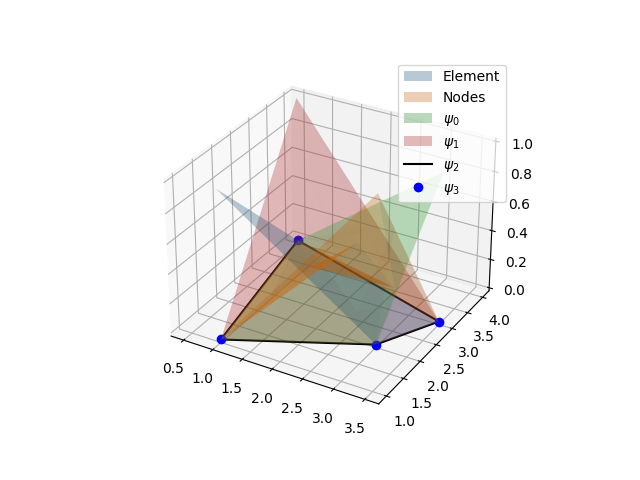
Triangular (3 nodes 2D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
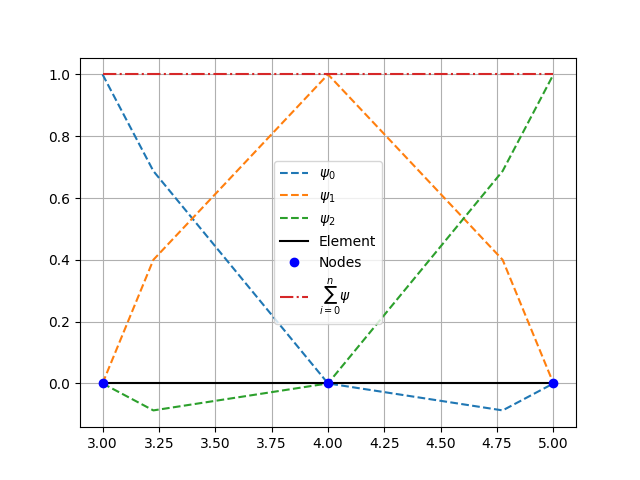
Line (3 nodes 1D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
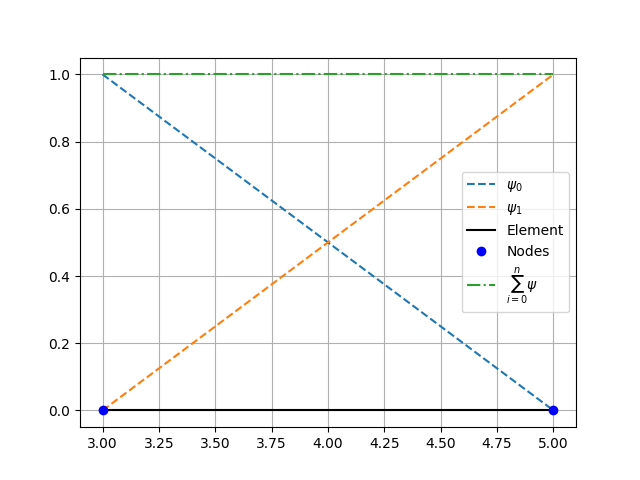
Line (2 nodes 2D) element coordinate transformation and shape functions.¶
Point inside element (works in all dimensions)¶
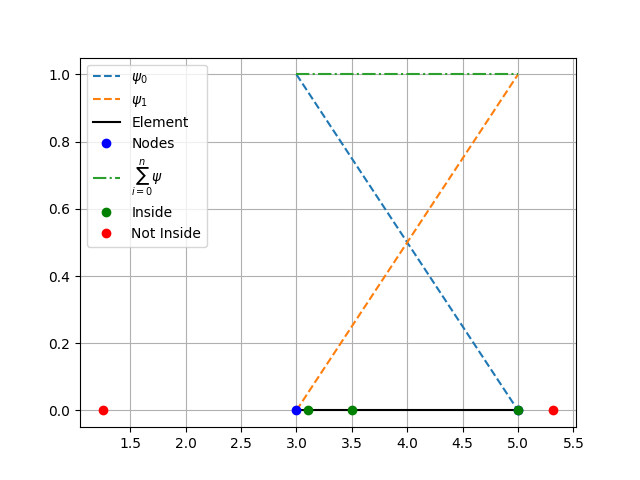
Test if given points are inside the element.¶
Jacobian graphs¶
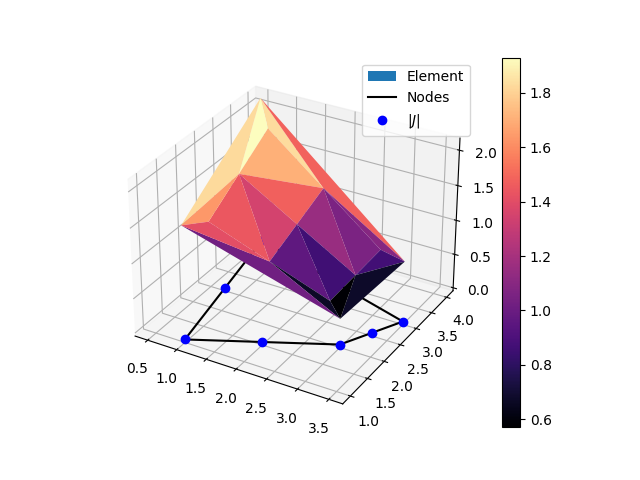
Serendipity (8 nodes 2D) element jacobian graph.¶
Quadrilateral (4 nodes 2D) element jacobian graph.¶
Triangular (6 nodes 2D) element jacobian graph.¶
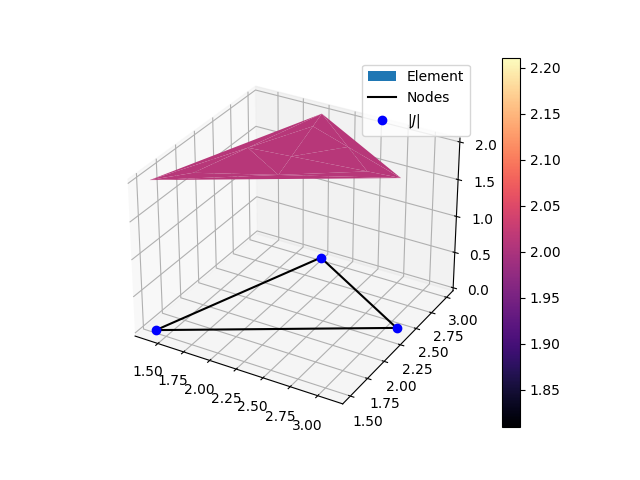
Triangular (3 nodes 2D) element jacobian graph.¶
Code¶
from FEM.Elements.E2D.Serendipity import Serendipity
from FEM.Elements.E2D.Quadrilateral import Quadrilateral
from FEM.Elements.E2D.LTriangular import LTriangular
from FEM.Elements.E2D.QTriangular import QTriangular
from FEM.Elements.E1D.LinealElement import LinealElement
from FEM.Elements.E1D.QuadraticElement import QuadraticElement
elements = []
coords = [[1, 1], [3, 2], [3.5, 3], [0.5, 4], [2, 1.5],
[3.25, 2.5], [(3.5+.5)/2, 3.5], [(0.5+1)/2, 5/2]]
gdl = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
eRS = Serendipity(coords, gdl)
eRS2 = Serendipity(coords, gdl)
elements.append(eRS)
coords = [[1, 1], [3, 2], [3.5, 3], [0.5, 4]]
gdl = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4]])
eRC = Quadrilateral(coords, gdl)
elements.append(eRC)
# [[-1.5, -1], [1, 0], [0, 5], [-0.25, -0.5], [0.5, 2.5], [-0.75, 2.0]]
coords = [[-1.5, -1], [1, 0], [0, 5]]
for i in range(len(coords)-1):
coords += [[(coords[i][0]+coords[i+1][0])/2,
(coords[i][1]+coords[i+1][1])/2]]
coords += [[(coords[i+1][0]+coords[0][0])/2,
(coords[i+1][1]+coords[0][1])/2]]
gdl = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]])
eTC = QTriangular(coords, gdl)
elements.append(eTC)
coords = [[1.4, 1.5], [3.1, 2.4], [2, 3]]
gdl = np.array([[1, 2, 3]])
eTL = LTriangular(coords, gdl)
elements.append(eTL)
coords = [[3], [4], [5]]
gdl = np.array([[3, 4, 5]])
e = QuadraticElement(coords, gdl, 3)
elements.append(e)
coords = [[3], [5]]
gdl = np.array([[3, 5]])
e = LinealElement(coords, gdl, 3)
elements.append(e)
# Coordinate transformation
for i, e in enumerate(elements):
e.draw()
plt.show()
# Point inside element
p_test = np.array([1.25, 5.32, 3.1, 3.5, 5.0])
result = e.isInside(p_test)
e.draw()
plt.gca().plot(p_test[result], [0.0] *
len(p_test[result]), 'o', c='g', label='Inside')
plt.gca().plot(p_test[np.invert(result)], [0.0] *
len(p_test[np.invert(result)]), 'o', c='r', label='Not Inside')
plt.legend()
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Inverse Mapping
z = eTL.inverseMapping(np.array([[1.3, 2.5, 3.5], [1.5, 2.6, 8.5]]))
# z = eTL.inverseMapping(np.array([[1.3],[1.5]]))
print(z)
# print(eTL.isInside(np.array([3.5,2.5])))
# Jacobian Graphs
for i, e in enumerate(elements):
e.jacobianGraph()
plt.show()
Examples.example10 module¶
Examples.example11 module¶
Examples.example13 module¶
Examples.example14 module¶
Examples.example15 module¶
Examples.example16 module¶
Examples.example17 module¶
Examples.example18 module¶
Examples.example19 module¶
Examples.example2 module¶
Geometry creation using triangles. Torsion2D¶
An I shape section when a unitary rotation is applied.
The input mesh is created using the Delaunay class using second order elements.
Geomery¶
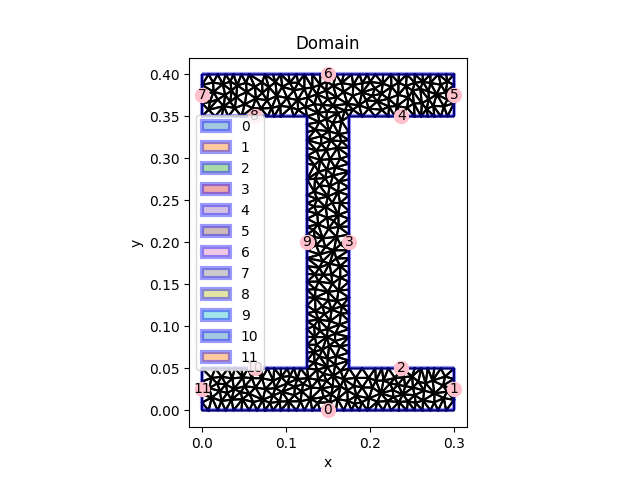
Input geometry created using Delaunay triangulations.¶
Result¶
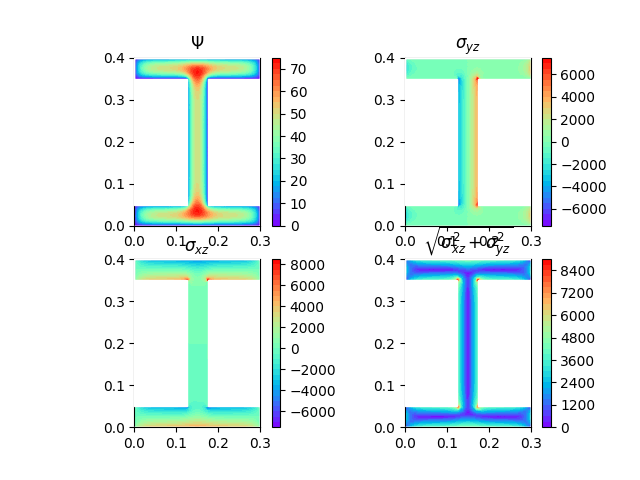
Analysis results.¶
Code¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from FEM.Torsion2D import Torsion2D
from FEM.Geometry import Delaunay, Geometry2D
a = 0.3
b = 0.3
tw = 0.05
tf = 0.05
E = 200000
v = 0.27
G = E / (2 * (1 + v))
phi = 1
# Geometry perimeter
vertices = [
[0, 0],
[a, 0],
[a, tf],
[a / 2 + tw / 2, tf],
[a / 2 + tw / 2, tf + b],
[a, tf + b],
[a, 2 * tf + b],
[0, 2 * tf + b],
[0, tf + b],
[a / 2 - tw / 2, tf + b],
[a / 2 - tw / 2, tf],
[0, tf],
]
# Input string to the delaunay triangulation.
# o=2 second order elements.
# a=0.00003 Maximum element area.
params = Delaunay._strdelaunay(constrained=True, delaunay=True,
a=0.00003, o=2)
# Mesh reation.
geometria = Delaunay(vertices, params)
# geometria.exportJSON('Examples/Mesh_tests/I_test.json') # Save the mesh to a file.
# geometria = Geometry2D.importJSON('Examples/Mesh_tests/I_test.json') # Load mesh from file.
# Show the geometry.
geometria.show()
plt.show()
# Create the Torsion2D analysis.
O = Torsion2D(geometria, G, phi)
O.solve() # All finite element steps.
plt.show()
Examples.example20 module¶
Examples.example21 module¶
Examples.example22 module¶
Examples.example23 module¶
Examples.example24 module¶
Examples.example25 module¶
Examples.example26 module¶
Examples.example27 module¶
Examples.example28 module¶
Examples.example29 module¶
Examples.example3 module¶
Geometry creation using triangles. Torsion2D¶
An square shape section when a unitary rotation is applied.
The input mesh is created using the Delaunay class using second order elements.
Geomery¶
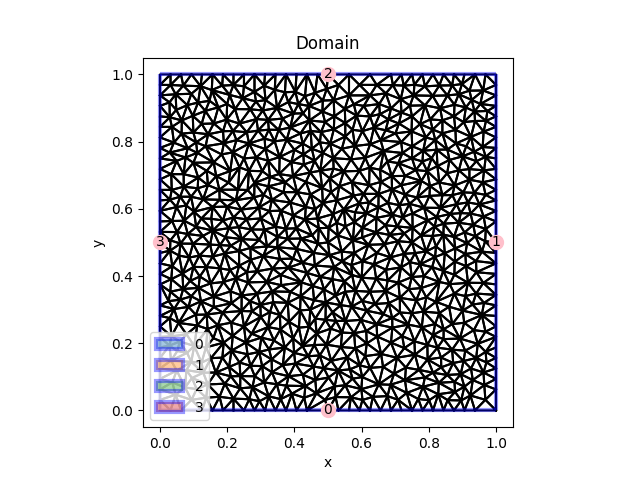
Input geometry created using Delaunay triangulations.¶
Result¶
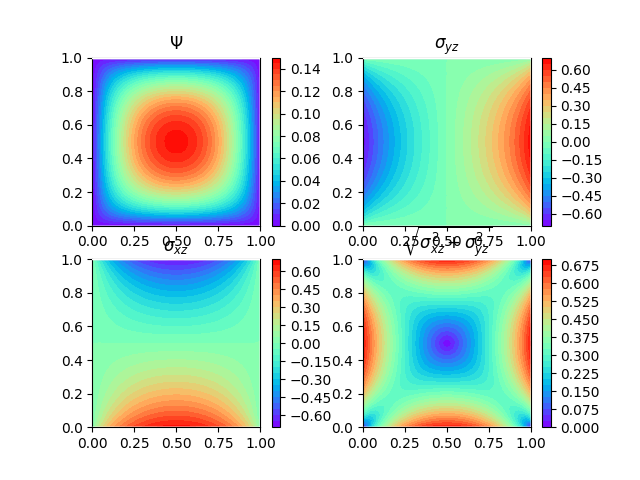
Analysis results.¶
Code¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from FEM.Torsion2D import Torsion2D
from FEM.Geometry import Geometry2D, Delaunay
a = 1
b = 1
E = 200000
v = 0.27
G = E/(2*(1+v))*0+1
phi = 1
# Use these lines to create the input geometry and file
# coords = np.array([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 1], [0, 1.0]])
# params = Delaunay._strdelaunay(a=0.0001, o=2)
# geo = Delaunay(coords, params)
# geo.exportJSON('Examples/Mesh_tests/Square_torsion.json')
geometria = Geometry2D.importJSON(
'Examples/Mesh_tests/Square_torsion.json')
geometria.show()
plt.show()
O = Torsion2D(geometria, G, phi, verbose=True)
O.solve()
plt.show()
Examples.example30 module¶
Examples.example31 module¶
Examples.example32 module¶
Examples.example33 module¶
Examples.example34 module¶
Examples.example35 module¶
Examples.example36 module¶
Examples.example37 module¶
Examples.example39 module¶
Examples.example4 module¶
Ordinary diferential equation 1D¶
The current file ust the general formulation of the EDO1D Class using custom function coeficients.
Geomery¶
Result¶
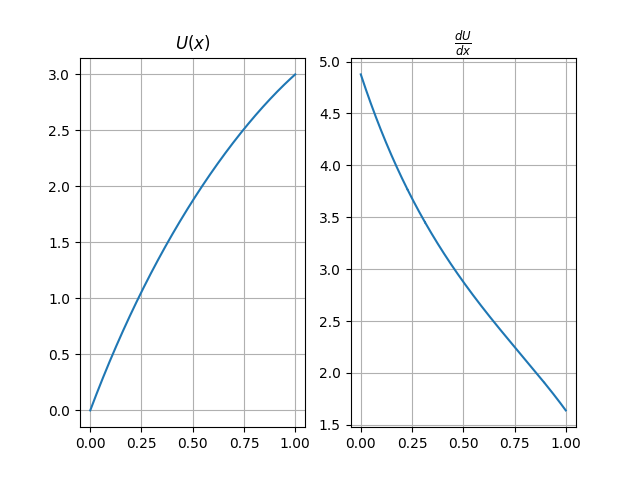
Analysis results.¶
Code¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from FEM.EDO1D import EDO1D
from FEM.Geometry import Lineal
# Define functions of the diferential equation
def a(x): return (x[0]**2-2)
def c(x): return (x[0]-3)
def f(x): return (x[0]**2-2)*6+(x[0]-3)*(3*x[0]**2)
# Define boundary conditions. List of boundary conditions. In the first node, value=0.0, in the last node, value = 3.0
cbe = [[0, 0.0], [-1, 3.0]]
lenght = 1
n = 500
o = 2
geometria = Lineal(lenght, n, o)
O = EDO1D(geometria, a, c, f)
O.cbe = cbe
O.solve()
plt.show()
Examples.example40 module¶
Examples.example41 module¶
Examples.example42 module¶
Examples.example43 module¶
Examples.example44 module¶
Examples.example45 module¶
Examples.example46 module¶
Examples.example47 module¶
Examples.example5 module¶
Examples.example51 module¶
Examples.example52 module¶
Examples.example53 module¶
Examples.example54 module¶
Examples.example55 module¶
Examples.example56 module¶
Examples.example57 module¶
Examples.example57 2D module¶
Examples.example57 2D 15 module¶
Examples.example58 module¶
Examples.example6 module¶
Test of point inside volumen (3D elements)¶
This example creates a 3D Brick element and test if a given set of points are inside the element.
Coords and gdls (degrees of freedom) are given by a Numpy ndarray matrix.
In the coordinate matrix, each row represents a node of the element and each column a dimension. For example, a 2D triangular element of 3 nodes must have a 3x2 matrix.
In the gdls matrix, each row represents a variable of the node and each column a node. For example, a 2D triangular element of 3 nodes and 2 variables per node (plane stress) must have a 2x3 gdls matrix.
Code¶
from FEM.Elements.E3D.Brick import Brick
import numpy as np
coords = np.array([[0, 0, 0.0], [1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0], [
0, 0, 1.0], [1, 0, 1], [1.5, 1.5, 1.5], [0, 1, 1]])
coords2 = coords + 1.5
gdl = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
e = Brick(coords=coords, gdl=gdl)
e2 = Brick(coords=coords2, gdl=gdl)
domain = e.T(e.domain.T)[0]
domain2 = e2.T(e.domain.T)[0]
points = np.array(
np.array([[-1, 0, 0], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]]).tolist()+domain.tolist())
r1 = e.isInside(points)
r2 = e.isInside(domain2)
print(r1, r2)
a = 0
Examples.example67 module¶
Examples.example68 module¶
Examples.example7 module¶
Creation of 3D elements¶
3D Elasticity beam problem using 8 node brick elements.
Code¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from FEM.Elasticity3D import Elasticity
from FEM.Geometry.Geometry import Geometry
E = 21000000.0
v = 0.2
h = 0.6
b = 0.3
L = 2.5
gamma = 23.54
_a = L
_b = h
_c = b
nx = 50
ny = 8
nz = 7
dx = _a/nx
dy = _b/ny
dz = _c/nz
coords = []
for i in range(nx+1):
x = i*dx
for j in range(ny+1):
y = j*dy
for k in range(nz+1):
z = k*dz
coords += [[x, y, z]]
dicc = []
def node(i, j, k): return i*(ny+1)*(nz+1)+j*(nz+1)+k
for i in range(nx):
for j in range(ny):
for k in range(nz):
node1 = node(i, j, k)
node2 = node(i+1, j, k)
node3 = node(i+1, j+1, k)
node4 = node(i, j+1, k)
node5 = node(i, j, k+1)
node6 = node(i+1, j, k+1)
node7 = node(i+1, j+1, k+1)
node8 = node(i, j+1, k+1)
dicc += [[node1, node2, node3, node4,
node5, node6, node7, node8]]
def fy(x): return -gamma
geometria = Geometry(dicc, coords, ["B1V"]*len(dicc), nvn=3, fast=True)
cbe = []
for i in range(len(coords)):
if 0.0 == coords[i][0]:
cbe += [[i*3, 0.0]]
cbe += [[i*3+1, 0.0]]
cbe += [[i*3+2, 0.0]]
geometria.cbe = cbe
O = Elasticity(geometria, E, v, gamma, fy=fy, verbose=True)
O.solve()
O.exportJSON('weird_beam.json')