FEM.Elements.E3D package¶
Collection of 3D Elements
Submodules¶
FEM.Elements.E3D.Brick module¶
BRICK ELEMENTS¶
Defines the lagrangian first order and second order brick elements
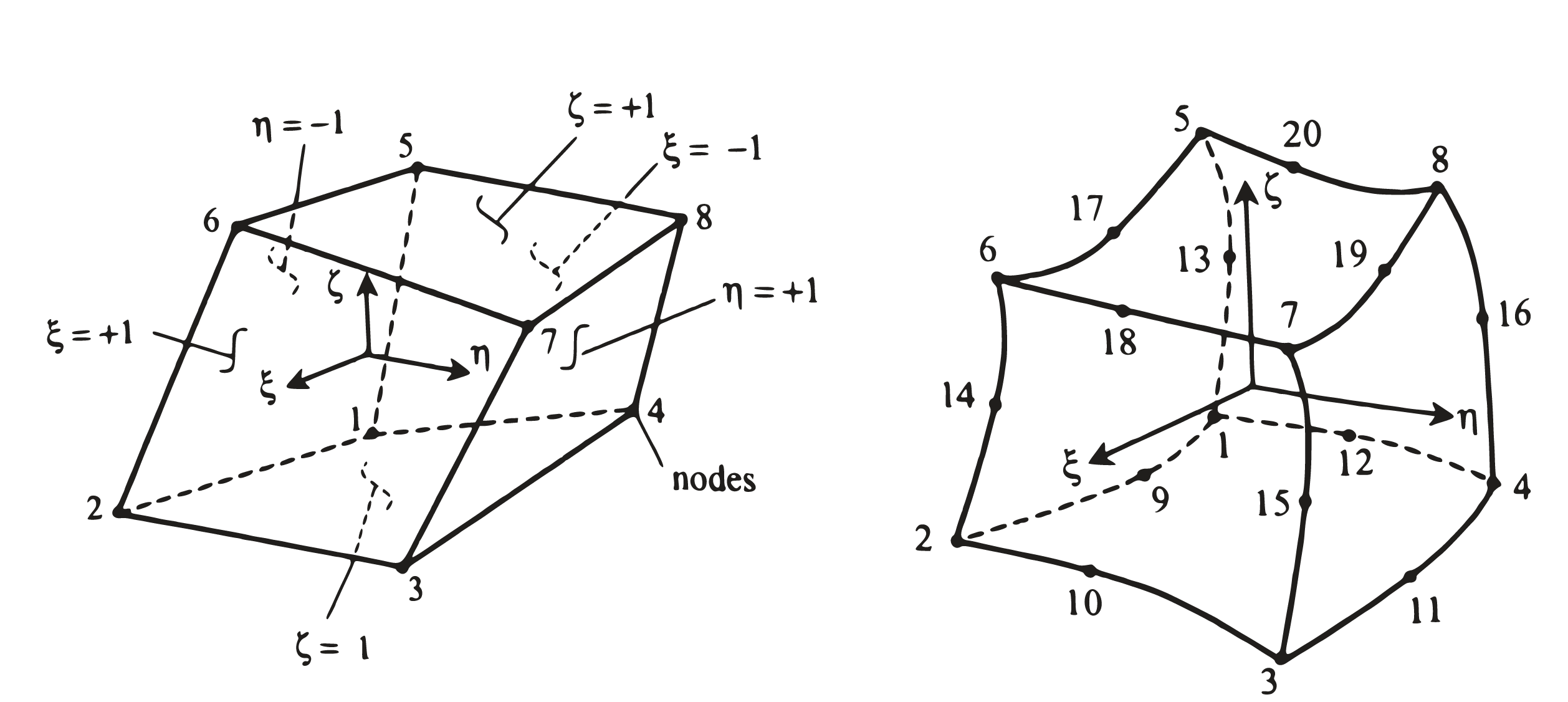
Brick (8 nodes) and BrickO2 (20 nodes). (Reddy, 2005)¶
Brick¶
First order 8 node brick element
Shape Functions¶
Shape Functions Derivatives¶
BrickO2¶
Second order 20 node brick element
Shape Functions¶
Shape Functions Derivatives¶
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.Brick.Brick(coords: ndarray, gdl: ndarray, n: int = 3, **kargs)¶
Bases:
Element3D,BrickSchemeCreates a 3D brick element
- Parameters:
coords (np.ndarray) – Node coordinates matrix
gdl (np.ndarray) – Degrees of freedom matrix
n (int, optional) – Number of gauss points used for integration. Defaults to 3.
- dpsis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions derivatives of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function derivatives evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- psis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.Brick.BrickO2(coords: ndarray, gdl: ndarray, n: int = 3, **kargs)¶
Bases:
Element3D,BrickSchemeCreates a 3D second order brick element.
- Parameters:
coords (np.ndarray) – Node coordinates matrix
gdl (np.ndarray) – Degrees of freedom matrix
n (int, optional) – Number of gauss points used for integration. Defaults to 3.
- dpsis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions derivatives of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function derivatives evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- psis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
FEM.Elements.E3D.BrickScheme module¶
Define the brick scheme used by brick elements
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.BrickScheme.BrickScheme(n: int, **kargs)¶
Bases:
objectGenerate a brick integration scheme
- Parameters:
n (int) – Number of gauss points
FEM.Elements.E3D.Element3D module¶
Defines a general 2D element
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.Element3D.Element3D(coords: ndarray, _coords: ndarray, gdl: ndarray, **kargs)¶
Bases:
ElementCreate a 3D element
- Parameters:
coords (np.ndarray) – Element coordinate matrix
_coords (np.ndarray) – Element coordinate matrix for graphical interface purposes
gdl (np.ndarray) – Degree of freedom matrix
- draw() None¶
Create a graph of element
- isInside(x: ndarray) ndarray¶
Test if a given points is inside element domain
- Parameters:
x (np.ndarray) – Point to be tested
- Returns:
Boolean array of test result
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- jacobianGraph() None¶
Create the determinant jacobian graph
FEM.Elements.E3D.Tetrahedral module¶
TETRAHEDRAL ELEMENTS¶
Defines the lagrangian first order and second order tetrahedral elements
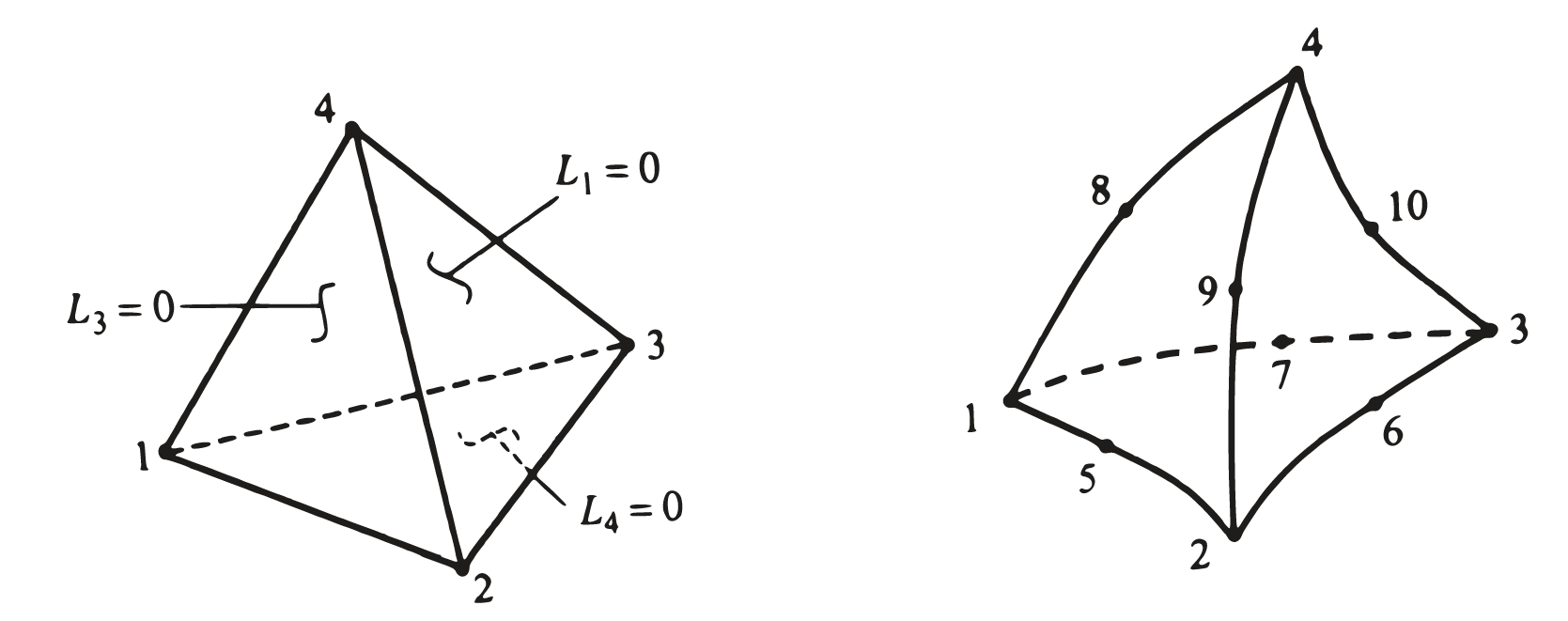
Tetrahedral (4 nodes) and TetrahedralO2 (10 nodes). (Reddy, 2005)¶
Tetrahedral¶
First order 4 node tetrahedral element
Shape Functions¶
Shape Functions Derivatives¶
TetrahedralO2¶
Second order 10 node tetrahedral element
Shape Functions¶
Shape Functions Derivatives¶
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.Tetrahedral.Tetrahedral(coords: ndarray, gdl: ndarray, n: int = 3, **kargs)¶
Bases:
Element3D,TetrahedralSchemeCreates a 3D tetrahedral element
- Parameters:
coords (np.ndarray) – Node coordinates matrix
gdl (np.ndarray) – Degrees of freedom matrix
n (int, optional) – Number of gauss points used for integration. Defaults to 3.
- dpsis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions derivatives of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function derivatives evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- inverseMapping(x0: ndarray, n: int = 100) ndarray¶
Give the natural coordinates of given global coordinates over elements using Newton’s method
- Parameters:
x0 (np.ndarray) – Global coordinates matrix
n (int, optional) – Máximun number of iterations. Defaults to 100.
- Returns:
Natural coordinates matrix
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- psis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.Tetrahedral.TetrahedralO2(coords: ndarray, gdl: ndarray, n: int = 3, **kargs)¶
Bases:
Element3D,TetrahedralSchemeCreates a 3D second order tetrahedral element
- Parameters:
coords (np.ndarray) – Node coordinates matrix
gdl (np.ndarray) – Degrees of freedom matrix
n (int, optional) – Number of gauss points used for integration. Defaults to 3.
- dpsis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions derivatives of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function derivatives evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- inverseMapping(x0: ndarray, n: int = 100) ndarray¶
Give the natural coordinates of given global coordinates over elements using Newton’s method
- Parameters:
x0 (np.ndarray) – Global coordinates matrix
n (int, optional) – Máximun number of iterations. Defaults to 100.
- Returns:
Natural coordinates matrix
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- psis(_z: ndarray) ndarray¶
Calculates the shape functions of a given natural coordinates
- Parameters:
z (np.ndarray) – Natural coordinates matrix
- Returns:
Shape function evaluated in Z points
- Return type:
np.ndarray
FEM.Elements.E3D.TetrahedralScheme module¶
Define the tetrahedral scheme used by tetrahedral elements
- class FEM.Elements.E3D.TetrahedralScheme.TetrahedralScheme(n: int, **kargs)¶
Bases:
objectGenerate a tetrahedral integration scheme
- Parameters:
n (int) – Number of gauss points